What is RSS?
RSS is an abbreviation for Rich Site Summary, Really Simple Syndication or just Real Smooth Stuff.
RSS is a format used to share short updates on the web. Many newspapers and medical sites offer RSS feeds, listing their latest news. It is the perfect way to stay on top of the new developments in the field you are interested in.
How to use RSS?
When you go to a website, just look for the orange RSS or XML icon, and then subscribe to the RSS feed by clicking on the icon. To read the RSS feeds, you need the Opera browser or a separate program called a news reader (feed aggregator). This program updates all feeds every hour, retrieving the RSS, so that the latest content from all selected sites is gathered in one place. And this is the biggest advantage of the RSS concept: you have all the news you want in one place, instantly, updated 24 x 7.
Update:
The best option for a RSS aggregator right now is Bloglines. It is website-based, free, easy and you don't have to install anything - it just works in your browser. If you have an internet-enabled PDA, the Bloglines Mobile feature is an excellent addition.
How does it work?
The 1-2-3 step process
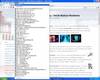
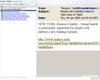
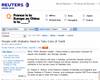
RSS Feeds menu in Opera browser; Single feed source during reading; Open the website article by clicking on the feed link
Why to use RSS? Give me an example.
For example, if a groundbreaking article is published in NEJM, you may not know about it unless you check the journal itself. If you use RSS feeds, you will notice that everybody is talking about this new thing on NEJM, and you will soon realize that this must be really good, so better go and check it. There was a recent study about the CRP and LDL use for risk stratification in CAD. The results were reviewed on all RSS feeds: NY Times, Wash Post, Boston Globe, CNN, Reuters Health, Medscape, WebMD, and medical blogs like Kevin MD and Journal Club. So much chatter usually indicates that something important has popped up. Also, the websites report not only on the results but what the researchers and their critics think about them. Not to mention the blogs written by your fellow physicians who also have their points of view on the news.
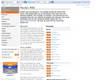


Subscribe to Reuters or NY Times RSS feeds by clicking on the red XML icons; RSS feed button on Kevin MD blog (first icon)
RSS feeds save time. You don't have to check 20 websites every day to stay updated. Just open Opera browser (or your RSS reader). If something new has been published on your monitored websites, it will appear in bold font. Then you check the short info, and if you are interested, only then you go to the website.
Above are the Opera screenshots showing the news reader in action. Check out the Flash demo showing how to subscribe to an RSS feed.
What program do I need to read RSS?
Internet Explorer does not support RSS yet but according to Bill Gates, this will come soon (probably in 2006). Mozilla Firefox needs a downloadable extension to check for RSS feeds. And of course, our favorite browser Opera, comes with an embedded RSS reader. The RSS feeds look exactly like your Favorites menu, with the difference that they are updated every hour and the info stays in your browser. By the way, this is not everything that Opera can do. The browser has the new voice technology and can read the articles to you. It also understands commands like "Go back", "Check next link”, and so on. With the size of only 3.5 MB, Opera is a small marvel (free with an ad banner, $ 39 to buy).
Bloglines is an online RSS aggregator, you just need to open a free account.
Podcasts are also distributed by RSS (by USA Today).
Suggested RSS feeds (all are free):
Reuters RSS, including RSS for their TV service
CNN RSS
National Public Radio (NPR) RSS - you can listen to the NPR feeds
NY Times RSS
Washington Post RSS
USA Today RSS
International Herald Tribune RSS
Medical RSS feeds
Getting RSS feeds for most medical journals - MedPDA.net uses the PubMed feeds to get RSS from all major journals
Medical Journals RSS-over 200 journals including NEJM, BMJ and others
Medscape RSS -you can subscribe to RSS updates in every subspecialty like cardiology, GI, ID, etc. (free registration required to read the full text on the Medscape website)
WebMD RSS
BioMed Central Journals are open access -permanently available online for free
American Medical News RSS (AMA)
PubMed offers RSS feeds for your querries
Local Weather - rssWeather.com
CompleteRSS - Search engine for RSS feeds. You can also search Google for a topic, newspaper or website name plus "RSS" in the search box
Resources:
RSS News on Demand - A Complete Guide - PC World - The best staring point
RSS readers offer new ways to keep up with the Web - USA Today
HOW TO: Getting Started with RSS - Paul Stamatiou
Listen to RSS for newbies - Future tense by NPR
RSS (protocol) - Wikipedia
News aggregator - Wikipedia
Syndicate yourself - PC World NZ
RSS: Hot Fix for Info-Junkies - Real Smooth Stuff - PC World
The Coming RSS Revolution - Forbes 2/04
RSS on Yahoo!
R|Mail brings RSS to your email




No comments:
Post a Comment